The article shows the 6 Major Types of Climate and Climate Zone in the World that affect the overall environment of the global world.
Scientists have classified Earth’s climate into zones since prehistoric times based on the length of the day and the sun’s height above the horizon. The Greek term “climate,” which describes the sun’s slant, is where the phrase originated. The main cause of variations in our planet’s climate is the unequal distribution of the sun’s heat over the surface. Climate is also greatly influenced by air circulation, precipitation patterns, proximity to the sea, and other so-called “climate-forming factors,” all of which are highly dependent on latitude and elevation above sea level. Climate-similar regions resemble wide swathes surrounding the globe.
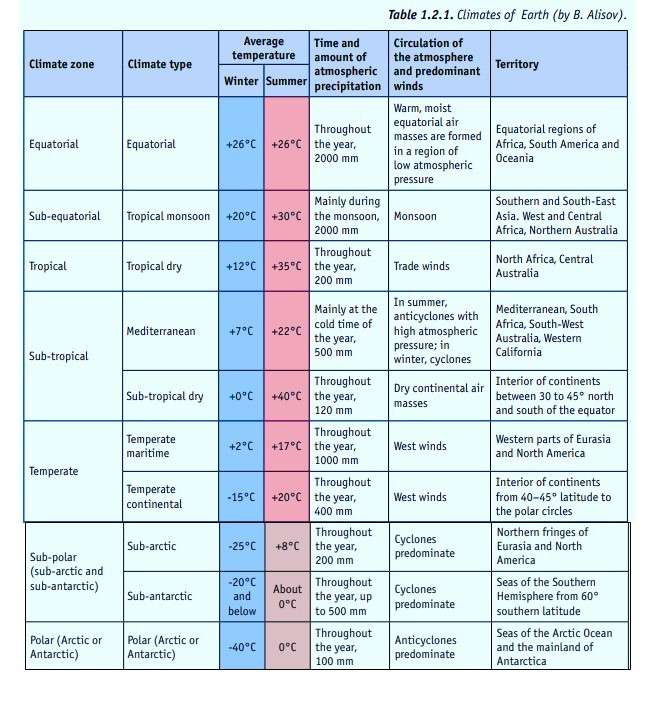
As described by Dansereau (1957) the world climate has been classified into six broad types.
- Equatorial Climate: Warm and humid equatorial air masses are indicative of an equatorial climate. The year-round temperature is consistently between +24 and +28 °C, and there is a lot of rain (between 1500 and 5000 mm). In an equatorial environment, rain falls more quickly than water can drain from the ground, resulting in soggy soil that is covered in a lush, towering rainforest. The majority of the Indonesian archipelago, the coasts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans in Asia, the Congo River Basin, the headwaters of the Nile in Africa, and the northern regions of South America all have equatorial climates. This climate is known for lack of seasonality which means that there is little fluctuation in temperature and precipitation. Northern South America (Brazil) and Central Africa (Sudan, Chad, Niger) have this kind of climate.
- Sub-equatorial climate: A sub-equatorial climate is characterized by a chilly, dry winter season that follows a wet season in July. In a sub-equatorial environment, the amount of rain varies greatly throughout the year. For instance, Conakry, the capital of Guinea, experiences 3920 mm of rain from June to September, but just 15 mm from December to March. This kind of climate may be found in South Asia, the tropical portions of Africa and South America, and some areas of the western Pacific and Indian oceans.
- Tropical Climate: Anticyclones with high pressure, which provide clear weather almost year-round, dominate tropical climates. The warm and cold seasons alternate. On the seaside, temperatures can range from +20 °C to +50 °C. Additionally, there can be significant daily temperature variations. For example, during the summer, the air can reach +40–45 °C in the day, while at night, it can drop to +10–15 °C.
- Temperate Climate: Temperate latitudes, extends from 40–45 degrees north and south of the equator to the polar circles, are home to temperate climates. More over half of the temperate zone is land, not sea, in the Northern Hemisphere. However, the ocean covers 98% of the Southern Hemisphere’s temperate zone. Cyclones cause frequent and severe weather changes, which are indicative of a temperate environment. There are four distinct seasons in a temperate climate: winter, summer, and autumn are the warmest and coldest, respectively. Spring and fall are considered transitional seasons.
- Sub-Polar Climate: In the Northern Hemisphere, a sub-arctic climate can be found between Arctic temperate climatic zones. Warm summer air masses and chilly winter air masses from the Arctic are characteristics of this climate. The summers are brief and frigid, with an occasional high of +15 °C during the day and lows of 0 to +3 °C at night in July. There is also a possibility of frosty evenings during the summer. Wintertime temperatures range from -35 to -45 °C throughout the day.
- Polar Climate: Polar climates are found in the Northern Hemisphere, north of 70 degrees latitude (Arctic climate), and in the Southern Hemisphere, south of 65 degrees latitude (Antarctic climate). All year long, polar air masses predominate. The term “polar night” refers to the period of time when the sun does not rise above the horizon, and “midnight sun” or “polar day” refers to the months when it does not set below the horizon.
- Desert Climate: This climate has the precipitation to evaporation remains very low. Temperatures may vary seasonally, but precipitation remains low for the whole year. Vegetation is typically small shrubs and ephemerals. Southern Arizona (Sonoran), Deserts in California (Mojave)and in other continents have this type of climate.
Also Read:
- Different Environment and Wildlife Acts in India Tourism Sector
- 3 Major Distribution of Physical Geography of India
- 6 Major Types of Climate and Climate Zone in the World
- 3 Traffic Conferences as per IATA in Tourism
- Tropical Wet and Dry Climate: India, Northern Australia, South-Eastern Asia, Central Africa and parts of South America have this kind of climate. This climatic zone is characterized by high temperatures throughout the year, with harsh wet and dry periods.
Comments are closed.